More
Safely Reveal Card Details to Customers
Sensitive card details such as the card number and security code are not returned in the responses of normal cards endpoints. Instead, Bridge provides a way for you to safely expose PANs to users in a way that keeps your servers out of PCI compliance scope.
The following is an overview of the steps you will need to take in order to implement this functionality:
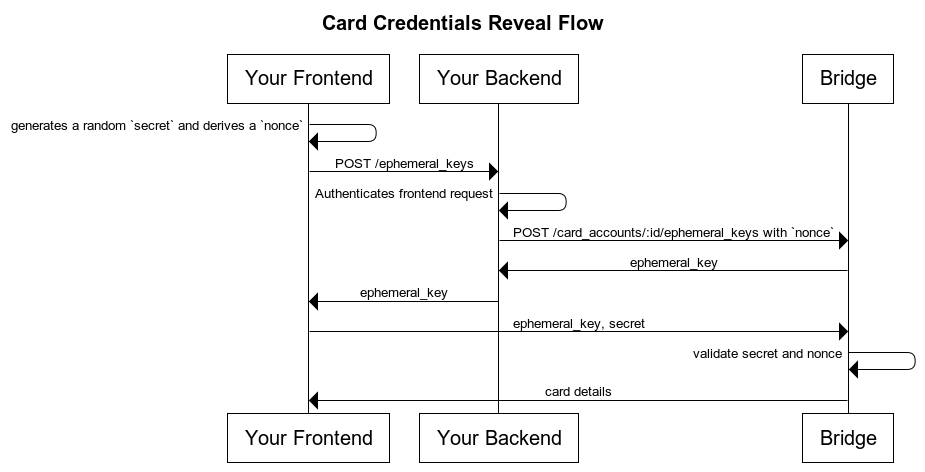 Below, we’ll discuss each of the steps in this flow in detail.
The client will send just the final
Note that Bridge has no ability to authenticate where the
Do not have your backend directly call Bridge to retrieve card credentials using this ephemeral key. Instead, it should pass this ephemeral key directly back to your frontend to perform the next step.
The client will include the original
Bridge will validate that the
This ephemeral key can only be used once, so the client will need to generate a new secret and nonce in order to show the card details again. In order to comply with PCI DSS requirement 3.4, you must not store the card details returned from this endpoint.
Below, we’ll discuss each of the steps in this flow in detail.
The client will send just the final
Note that Bridge has no ability to authenticate where the
Do not have your backend directly call Bridge to retrieve card credentials using this ephemeral key. Instead, it should pass this ephemeral key directly back to your frontend to perform the next step.
The client will include the original
Bridge will validate that the
This ephemeral key can only be used once, so the client will need to generate a new secret and nonce in order to show the card details again. In order to comply with PCI DSS requirement 3.4, you must not store the card details returned from this endpoint.
- Your backend implements an endpoint to generate an ephemeral key for your customer.
- Your frontend will generate a random secret, and use it to generate a nonce, which will be passed through your backend and then to Bridge to generate a one-time ephemeral key.
- Your frontend will then directly call a special Bridge endpoint with this ephemeral key as the credential, and provide the original secret to prove ownership.
- Bridge will then reveal the card number, security code, and expiration date directly to the frontend, without any sensitive card details passing through your backend.
 Below, we’ll discuss each of the steps in this flow in detail.
Below, we’ll discuss each of the steps in this flow in detail.
1. Client derives a Nonce and sends it to your backend
Your client generates a secret, and usesSHA-256 to generate a nonce from the secret, and a deterministic string nonce:{timestamp}. As this needs to be done in a particular way, you can use the following snippets in your client as a reference:
nonce from each of these snippets to your backend.
It will then reserve the original clientSecret and clientTimestamp it used to generate the nonce, as it will need to be used validate the ephemeral key in step 4 below. The client must not store or reuse the secret or timestamp.
2. Your backend relays the Nonce to Bridge
Your backend will then send the derived nonce to Bridge byPOSTing to /v0/customers/{customerId}/card_accounts/{cardAccountId}/ephemeral_keys. The request should contain just the client nonce itself, like so:
client_nonce is actually from. The responsibility is on your backend to authenticate that the nonce was sent from the right customer to access the right card account.
3. Bridge generates a one-time Ephemeral Key associated to the Nonce
The response returned by Bridge in/v0/customers/{customerId}/card_accounts/{cardAccountId}/ephemeral_keys will contain just one field, ephemeral_key, which contains a token that can be used once to reveal the card details. This token expires in 5 minutes.
Here is an example of the response:
4. Your frontend directly calls Bridge with the Ephemeral Key, Nonce, and Secret
To reveal the card credentials, your frontend will directly call a special Bridge endpoint. This endpoint does not require a Bridge API key, and instead requires just ephemeral key itself in theAuthorization header as the credential, like so:
clientSecret and clientTimestamp used to generate the nonce as query parameters in the requested URL, like so:
ephemeralKey is associated with the nonce derived from the same clientSecret and clientTimestamp. It will also validate that the ephemeral key has not already been used, and that the key hasn’t expired yet.
This endpoint will return a response similar to the following:
